Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd” – Shweta Kodad
Shweta Kodad
Diplomová práce
Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd”
Abstract:
INTRODUCTION The social responsiveness of the Indian democracy toward all its residents is thought to be the key to its true success. However, due to its limited resources, the nation works incredibly hard to extend the facilities and advantages to all social strata to retain a true and thriving democracy. To guarantee a higher level of living for its citizens, the Government of India requires assistance from the corporate sector. In this regard, corporate India is anticipated to play a positive role by engaging in initiatives that could eventually result in social renewal, development, and the empowerment of underprivileged individuals. If this occurs, India will be quite happy to be one of the nations to achieve inclusive growth. As a result, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) actions of firms are a true key to overcoming both economic and social inequalities, which benefits the person in the last mile. Additionally, corporate India is required by the 2013 Companies Act to work toward a growth-based socioeconomic and environmental development paradigm. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a company system that makes it possible to produce and distribute money for the benefit of its stakeholders by putting in place and integrating moral frameworks and environmentally friendly business practices. In other words, CSR refers to methods through which businesses or corporations conduct their operations in a morally upstanding, considerate of society, and developmentally advantageous manner. As a result, CSR has been viewed as a competitive advantage for businesses that fulfill their social obligations. From the standpoint of both foreign and local investors, firms tend to improve their reputation as responsible corporate citizens by engaging in CSR initiatives. Consumers are increasingly aware of corporations' responsibilities today thanks to improved education and the media's impact. Business organizations may no longer be allowed to ignore CSR. The purpose of business in society is no longer just to make money; it is also to treat stakeholders with respect. Businesses are currently under constant pressure from a variety of stakeholders, such as employee pressures to uphold specific employee rights at work, consumer pressures to prevent price increases and produce safe products, and community and environmental pressures to ensure that business operations do not jeopardize community safety. Corporations feel it unavoidable to turn to CSR because of all these pressures from many stakeholders. Bellary under Kalyana Karnataka Territory: The Nizams of Hyderabad ruled the Hyderabad-Karnataka region long after India attained independence (1947), united with Indian Union on September 17, 1948. The name "Kalya" (or "Kalyana Karnataka") derives from the Kingdom of Kalyana, which served as the focal point of the Sharana movement and where Basvanna and other social reformers, like Vachana Sahitaya, adhered to his teachings. B.S. Yediyurappa, the chief minister of Karnataka, officially declared the area to be known as Kalyana Karnataka. Six districts in Karnataka's northeast Bidar, Kalaburagi, Koppal, Ballari, Yadgir, and Raichur. The CM made the declaration "Hyderabad-Karnataka Liberation Day.". The region enjoys special status under Article 371J of the Indian Constitution. The first national conference on CSR was held in 2012 to examine and discuss CSR in the context of India (Ray and Raju, 2014). According to Ray and Raju (2014), a shift away from donations and aid and toward a more organized CSR is taking place. They continue to use initiatives as examples rather than a broader definition of CSR as a component of corporate management and strategies. However, many businesses are incorporating CSR into their organizational framework (Perspectives of Business, 2007 in Ray and Raju, 2014). Corporations appear to be realizing that CSR is not just an expense but also a crucial component of their brand and may even help them defend them …víceméněAbstract:
selves from competition. 500 Indian companies participated in Karmayog's research (2010 in Raju, 2014), which revealed that CSR procedures have improved, awareness has risen, and reporting has increased. The government's decision to alter the law, on the other hand, is one of the most intriguing developments in this area. Companies that come under a specified category are required to dedicate 2% of their net profit to CSR as of 2015. The government's most recent decision will undoubtedly alter CSR. The government's most recent decision will undoubtedly alter CSR. Companies having at least Rs. 5 crore (about 700.000 Euros) in net profit, Rs. 1,000 crore (around 140 million Euros) in revenue, or Rs. 500 crore in net worth will be required to spend money on CSR (approximately 70 million Euro). Companies in these categories are required to dedicate 2% of their net profit to CSR (Indian Express). The estimation is that about 8.000 companies in India apply to the mandatory spending of 2% (Business Standard). As part of the movement towards implementing CSR in India, Tata institute of Social Sciences (TISS) and the Department of Public Enterprises (DPE), government of India developed a centralised system. TISS is now hosting the National CSR Hub which core functions are research, publication, knowledge dissemination, capacity building and advocacy (CSR Hub). Community development Community development policies always place a strong emphasis on the social and economic advancement of rural, urban, and tribal populations. Both the state and the federal governments in India continue to work on creating and implementing community development programs. After the Companies Act was implemented in India, the idea of community development was reframed to include contemporary development theories. Community development initiatives have benefited from business sector intervention. The new components were suggested by the Companies Act program development guidelines for community development. The main areas of focus for community development by corporations in India now include social business projects, rural, urban, and tribal development, and CSR activities components like health, education, literacy, and empowerment. In Bellary there are 266 iron ore mines in Karnataka, 134 ore located in forest areas. In the Bellary District, in this area are abundant. Both metallic and non-metallic minerals are present. Iron ore, manganese ore, red oxide, gold, copper, and lead are among the metallic minerals. To its credit, Bellary is home to the second-largest single rock mountain in the entire globe. Bellary Agriculture is the district's primary industry, and 75% of the labour force there depends on it for a living. The main source of irrigation is Tungabhadra Dam,148 mines (out of which 98 are in forest areas) cover 10,598 hectares of land. in the 1993 National Mineral Policy that began encouraging private players to participate in iron ore mining. For my thesis I have selected two companies which are vast hand in community development through CSR The Sandur Manganese and Iron Ores limited (SMIORE) It established in 1964, The company is one of the largest miners of manganese ore in India and is estimated to hold reserves of 7.83 million tonne. The Company’s Corporate Social Responsibility philosophy support with it's core values of improving the lives of people living in and around Sandur, SMIORE has been consciously contributing towards social development and environmental protection. The SMIORE CSR schemes and programmes are anchored on five pillars: health, education, environment, area development and protection of heritage and art. SMIORE has been in Top companies when considered CSR spent in Bellary region mainly focusing on Education and Rural Development KIOCL Limited KIOCL Limited (Formerly known as Kudremukh Iron Ore Company Limited), a Flagship Company under the Ministry of Steel, Govt. of India was found on 1976 for mining and beneficiation of low-grade iron ore at Kudremukh, Karnataka, India. KIOCL is government company and has been another top public organization when considered CSR spent in Bellary region mainly focusing on Education and Environment Well first, a community is "usually defined as a collection of people sharing a shared goal" who are "interdependent for the fulfillment of certain requirements" and who reside close by and regularly interact." All group members have responsibilities that are delegated based on mutual expectations. The group values and respects the uniqueness of other people in the neighborhood. A sense of community, which is defined as the emotions of duty to and for others as well as oneself, open communication, and devotion to the group welfare, exists in a community. Community leaders are people who work to persuade others to accept responsibility for their decisions, their successes, and the welfare of the community. Community development (CD) refers to initiatives carried out by a community in collaboration with external organizations or corporations. These programs empower people and "groups of people" by giving them the resources they need to bring about change in their own neighborhoods. And the objective of my thesis, explore and analyse the nature of firm CSR and its initiatives impact on the Community development from FY 2014 till FY 2021 on Bellary, Karnataka To examine the effects of CSR practice of the firm “The Sandur Manganese and Iron Ores limited” “Kudremukh Iron Ore Company limited” hereafter referred as “SMIORE” and KIOCL Limited on the firms reputation To Identify the effects of the CSR spent on the net profit of SMIORE and KIOCL between 2014 to 2021. To analyze the impact of CSR on social and environmental development in Bellary region between 2014 to 2021. Literature Review: The study makes use of ideas and tries to investigate how community development has helped enhance rural livelihood in India. It is carried out using secondary data and a review of the literature, allowing the analysis, discussion, and conclusion to be done considering the body of prior knowledge. According to the nature of the research question, qualitative research was used to perform the study. It is particularly significant for this study since community development in rural regions is based on insights from the social and behavioral sciences and works with the people to alter not only lifestyle but also systems. policies, and built environment, hence it is clear that qualitative research is useful in this context. As a result, the dissertation has been conducted using descriptive research methods. However, the study is also backed by quantitative approach using the case study on Self-Help Groups in Karnataka, India to better understand the role of community development. The research articles reviewed below were from reputable national and international journals, PhD theses, reference books, etc., and they covered a variety of CSR-related topics. The origins of the stagnation of economic life in rural areas are a challenge that developing countries are attempting to overcome with varied degrees of success (Todaro, 1985). The application of computing power to the management of rural development is an information-intensive activity that has long been seen as having enormous potential utility. Information technology has received a lot of attention as a vital resource in promoting Socio-economic development (UN, 1986; Munasinghe, 1989). More businesses are realizing the value of CSR and actively participating in CSR activities including corporate charity and ethical advertising (Wang, 2007). In the context of this study, the impact of CSR on community development includes any direct and indirect benefits that the community receives because of corporate social responsibility efforts on the community as a whole and the social system. ISMAIL (2009) states the same thing. Community development (CD) refers to initiatives carried out by communities in collaboration with outside agencies or businesses to empower individuals and groups of people by giving them the tools they need to bring about change in their own neighborhoods. However, businesses are urged to actively engage in CSR because it affords them the chance to play significant roles in society (Mark-Herbert and Von Schantz 2007 in Nilson, 2005; Ruggie, 2002). Veludo-de-Oliveria (2006) emphasized the ongoing discussion surrounding the contribution of business to community development and asserted that "businesses are concerned with their clients and it is about time they handled society as a whole in the same manner." In a same line, Nwachukwu (2006) made it abundantly evident that the society will degenerate unless the same significance that is accorded to profit by corporations is attached to CSR. This demonstrates unequivocally how arguments for and against social responsibility that have surfaced over time are connected. Together, they represent most of the public's perception that business has obligations to society beyond the traditional economic role it historically played. Then, corporate social responsibility just sets the consensus. And the fusion of the concepts of "Development" and "community". The debate over what makes a community and how to define it never ends, but the definition of the term as it relates to "human ecology," "systems theory," and "field theory" is the most crucial angle for this investigation. According to Luloff and Krannich (2002, referenced by Matarrita 2012: 293–305), community is defined as a "system of relationship" through which locals interact and fulfill their everyday needs. The strategy is focused on community organization. Larger Indian firms have developed systematic approaches to CSR initiatives in modern times. Many of the business activities in India that have been embraced are blatant copies of Western ideas of CSR or philanthropy. In his 2013 research paper, "Defining the Role Engagement of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)," Benjamin James Inyang examined different CSR initiatives carried out by SMEs, as well as their role in CSR implementation and how it benefits developing nations. It was discovered that SMEs were concentrating their CSR operations toward supply chain requirements, employee initiatives, consumption, and community development. According to the study, the government should provide the necessary incentives and support services to effectively engage SME in CSR. according to Humphreys (2000), community relations and development are critical for an organization to engage with essential stakeholders and protect its business interests. In line with this study, Kemp and Owen (2013) .CSR actions carried out by businesses for the community are beneficial to sustainable development, and businesses' interests ought to be in line with those of the community (Humphreys, 2000; Kemp and Owen, 2013; Sharma and Bhatnagar, 2015). Mining operations have a detrimental effect on agricultural land, forests, and water supplies, making it more challenging for people to improve their standard of living (Tiamgne et al., 2022). Improved relationships between businesses and communities are underlined as one of the key advantages of CSR. Degie and Kebede claim (2019) Mining organizations therefore need to integrate corporate social responsibility (CSR) into their business policies to mitigate the negative impact of mining on the socio-economic environment (Esteves, 2008; Eweje, 2006; Keith, 2012). In their article "Corporate Social Responsibility and Education in India," Chopra, Abha, and Marriya Shruti (2013) concentrated on CSR initiatives aimed at the education sector. Companies have made an effort to take into account the difficulties that education faces, such as standardized testing, tight budgets, teacher retention issues, and competition for workers around the world, and have focused on the parts of the education sector that are relevant to their corporate objectives. Based on stakeholder theory, Akinyomi, Oladele John (2013) investigated the practice of corporate social responsibility by manufacturing companies in Nigeria. Education and youth development/sport are two of the main focuses of CSR initiatives, according to the report. The survey also showed that, in relation to the companies' turnover, investments in CSR initiatives were insignificant. In his article "Corporate Social Responsibility in Nepal," Krishna Kumar Shah (2012) covered the conceptual side of social responsibility and its significance in Nepal. Additionally, it has placed emphasis on how businesses should abide by the law, become inspired to take part in activities that advance society, and support governmental and social organizations as they deal with issues like environmental dangers, unemployment, poverty, and others. In their work titled "Corporate Social Responsibility: Does It Matter?" Wickramasinghe, D.W.A. (2012) attempted to investigate the influence and connection between social responsibility and the success of the chosen manufacturing businesses in Sri Lanka. Six important factors—economic, personal, product, environmental, discriminatory, and community involvement of social responsibility—were taken into consideration when examining the link. A questionnaire and handbook of chosen manufacturing companies were used to get the data. Return on investment (ROI) of the company was used as a technique to gauge each company's success. Various statistical approaches have been employed to determine the connection between a company's success as measured by ROI and its commitment to social responsibility in his study paper "Company Social Responsibility and political agenda of the corporate," Surendra Pratap (2011) claims that He claims that CSR strives for financial success. Tax exemptions provide an immediate financial gain. The voluntary aspect of CSR, however, leads to corporate choosing only those initiatives that successfully enhance the company's brand image and those initiatives that directly assist the business. Numerous NGOs have collaborated with businesses through working with CSR auditing firms, and many more have done so by supporting CSR studies and campaigns. As a result, these NGOs are doing everything they can to uphold CSR and get little criticism to retain a neutral reputation. In this article from 2010, Sanjay Pradhan and Akhilesh Ranjan analyze corporate social responsibility practices in rural development. They have researched the CSR policies of 14 public and private Indian businesses for rural development. Secondary data was employed as the approach. Their research sought to determine if corporations saw rural residents as stakeholders. And if the answer is yes, what CSR activities are being implemented by businesses for rural development, and do they consider this to be a component of their business strategy? According to the data, CSR initiatives performed by organizations have a good effect on both their business and rural development. In their 2009 study titled "Corporate Social Responsibility: The Key Role of Human Resources Management," Suparna Sharma et al. tried to investigate the involvement of HRM professionals in corporate social responsibility. They have concluded that the combined influence of CSR and human resource activities can significantly contribute to long-term performance in firms by supporting employees' desirable behavior. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Introduction CSR is not a new concept in India; organizations like Infosys, TCS, Reliance, and Birla have been incorporating charitable work into their operations for many years. Despite these businesses, CSR in Karnataka, India, is still quite young. CSR is still not institutionalized by the businesses in Karnataka. Companies in the public sector and those with global presences engage in CSR as a core component of their operations. Few businesses participated in social programs. However, the Companies Act of 2013 makes CSR actions for businesses required. The current issue is determining which direction businesses should concentrate their efforts when implementing social initiatives and how managers are acting about CSR. Research is conducted and a problem statement is established to study the problem. The study's two main objectives are to gauge managers' acceptance of and implementation of CSR and to examine the CSR operations of several mining businesses in the Bellary region of Karnataka. The research's methodology is presented in this chapter. Describe the research approach that will be used in the current study is the general goal of this chapter. The overall strategy of a structured process for compiling accurate and trustworthy material for the purpose of investigations is laid out in research methodology. To comprehend a phenomenon and generalize data gleaned from the population, a systematic process of information gathering from a population is used. The study's design, study population, sampling methods, data collection tools, source of the data, ethical considerations, instrument dependability, data analysis, and organizational profiles of SMIORE and KIOCL are all presented. Significance of study The broad research question that the current study attempts to address concerns that need to be answered are whether CSR is institutionalized and spread throughout the business from top to bottom or if just the top management is active, even though CSR is a topic that receives significant discussion in the corporate sectors. • Do businesses approach CSR holistically and regard it as a system rather than a collection of discrete activities? • Do organizations properly focus on CSR from all angles? The reach and effectiveness of CSR programs are further hampered by a lack of knowledge, inadequately trained staff, a lack of accurate data, and a lack of precise information on the types of CSR activities, coverage, and policy, among other factors. The study is an effort to find the answers to the questions raised above. Definition of research problem statement The following queries can be used to express the same. 1. Companies have engaged in CSR initiatives, which are emphasized as well, but do the businesses adhere to correct CSR practices and have a comprehensive understanding of CSR? 2. What do the management of enterprises in the mining sector think about implementing corporate social responsibility? 3. What social responsibility practices have specific mining industry businesses adopted? Do they differ substantially from other industries? The queries inspired some additional investigation. To quantify the research, a thorough investigation was conducted, and two groups of areas were found. Firstly, how do businesses behave? Whether they adhere to 26000 or other international standards? What are the managers' perspectives on the application of CSR, and what is the second set? The foundation for additional investigation has been supplied by the continuing research. The operational aspect of social responsibility, social aspect of social responsibility, environmental component of social responsibility, and social development aspect of social responsibility are only a few of the themes covered in the first set of questions. And using Voyant techniques, a thorough examination of numerous annual and sustainability reports was conducted. The necessity for and justification for social responsibility, methods of putting social responsibility into effect, and finally implementation and practice of social responsibility have all been extensively examined in the second category. A study of CSR activities of chosen enterprises in Bellary, Karnataka, is the problem statement that results from the division of the primary problem into several subproblems and a variety of sets of questions connected to the subproblems. Objective of the study 1) To research the comprehensive approach taken by chosen corporations to CSR initiatives. 2) To analyse the environmental, social, economic, and operational practices of the chosen mining sector corporations in four categories, with a focus on social responsibility. 3) Developing systematic data based on managers' perceptions of the necessity and logic of taking social responsibility. 4) To learn what managers think of various social responsibility strategies. 5) To understand the managers' perspectives on execution and social responsibility Research Design The study is based on a detailed analysis of the CSR initiatives of the organizations and a measurement of managers' attitudes about accepting and putting CSR into practice. Since opinions of the managers were gauged by a structured questionnaire and numerous annual reports and sustainability reports were analysed from 2014 to 2021, a detailed study is carried out utilizing a mixed-methods (qualitative and quantitative) descriptive research methodology. Population of the Study All businesses with a revenue of at least Rs. 500 crore and those required to participate in CSR under the 2013 Companies Act comprise the study's sample. It could belong to any industry and be situated anywhere in the Indian state of Karnataka. Sample frame The large-scale businesses with operations in Bellary make up the sample frame. Sample size The sample consists of 104 managers, of which 88 are medium level managers and 16 are high level managers. Sources of data Data from both primary and secondary sources have been gathered. For gauging managers' opinions, primary data was gathered via a structured questionnaire, while secondary data came from annual reports, sustainability reports from the companies, various research papers and publications, websites, etc. Data collection tools Since both primary and secondary data must be gathered, a personal and mail survey was sent to reputable businesses to gather primary data. For examining managers' attitudes toward exercising social responsibility, mail questionnaires were delivered through courier and e-mail to the company managers, and secondary data was gathered from annual reports, sustainability reports, research papers, and publications. Design of questionnaire 10 executives from a sample of selected large businesses who are in the sample are given the questionnaire. The questionnaire is condensed and limited to two primary areas of what managers believe and how the organization operates considering the experience obtained during the pilot survey. The final set of surveys asks managers 12 questions in all. There are two categories of questions on the survey: (a) Questions with a Yes/No response option. These inquiries are meant to gather managers' opinions on what motivates businesses to engage in social responsibility. There are four of these questions in the questionnaire. (b) Questions that are designed to elicit responses using a Likert-type scale, where quantification is desired in terms of the degree of significance or agreement. The scale is described as follows: 5- Strongly agree 4-Agree 3-Uncertain 2-Disagree 1-I completely disagree The respondents are instructed to carefully read the statements and mark the number that best reflects their judgment of agreement or importance by placing an X. …víceméně
Jazyk práce: angličtina
Datum vytvoření / odevzdání či podání práce: 4. 4. 2023
Obhajoba závěrečné práce
- Obhajoba proběhla 23. 5. 2023
- Vedoucí: doc. Ing. Irena Jindřichovská, CSc.
- Oponent: Jaroslav Halík, externi
Citační záznam
Citace dle ISO 690:
KODAD, Shweta. \textit{Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd”}. Online. Diplomová práce. Praha: Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakulta. 2023. Dostupné z: https://theses.cz/id/tv4oql/.
KODAD, Shweta. <i>Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd”</i>. Online. Diplomová práce. Praha: Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakulta. 2023. Dostupné z: https://theses.cz/id/tv4oql/.
KODAD, Shweta. Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd”. Online. Diplomová práce. Praha: Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakulta. 2023. Dostupné z: https://theses.cz/id/tv4oql/.
@MastersThesis{Kodad2023thesis,
AUTHOR = "Kodad, Shweta",
TITLE = "Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd” [online]",
YEAR = "2023 [cit. 2024-11-09]",
TYPE = "Diplomová práce",
SCHOOL = "Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakultaPraha",
NOTE = "SUPERVISOR: doc. Ing. Irena Jindřichovská, CSc.",
URL = "https://theses.cz/id/tv4oql/",
}
AUTHOR = "Kodad, Shweta",
TITLE = "Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd” [online]",
YEAR = "2023 [cit. 2024-11-09]",
TYPE = "Diplomová práce",
SCHOOL = "Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakultaPraha",
NOTE = "SUPERVISOR: doc. Ing. Irena Jindřichovská, CSc.",
URL = "https://theses.cz/id/tv4oql/",
}
@MastersThesis{Kodad2023thesis,
AUTHOR = {Kodad, Shweta},
TITLE = {Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd”},
YEAR = {2023},
TYPE = {Diplomová práce},
INSTITUTION = {Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakulta},
LOCATION = {Praha},
SUPERVISOR = {doc. Ing. Irena Jindřichovská, CSc.},
URL = {https://theses.cz/id/tv4oql/},
URL_DATE = {2024-11-09},
}
AUTHOR = {Kodad, Shweta},
TITLE = {Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd”},
YEAR = {2023},
TYPE = {Diplomová práce},
INSTITUTION = {Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakulta},
LOCATION = {Praha},
SUPERVISOR = {doc. Ing. Irena Jindřichovská, CSc.},
URL = {https://theses.cz/id/tv4oql/},
URL_DATE = {2024-11-09},
}
{{Citace kvalifikační práce
| příjmení = Kodad
| jméno = Shweta
| instituce = Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakulta
| titul = Corporate Social Responsibility On Community Development in Bellary, Karnataka, India case study of “SMIORE”and “KIOCL Ltd”
| url = https://theses.cz/id/tv4oql/
| typ práce = Diplomová práce
| vedoucí = doc. Ing. Irena Jindřichovská, CSc.
| rok = 2023
| počet stran =
| strany =
| citace = 2024-11-09
| poznámka =
| jazyk =
}}
Plný text práce
Obsah online archivu závěrečné práce
Zveřejněno v Theses:- světu
Jak jinak získat přístup k textu
Instituce archivující a zpřístupňující práci: Česká zemědělská univerzita v Praze, Provozně ekonomická fakultaČeská zemědělská univerzita v Praze
Provozně ekonomická fakultaMagisterský studijní program:
Economics and Management
Práce na příbuzné téma
Seznam prací, které mají shodná klíčová slova.
Název
Vložil
Vloženo
Práva
Složky
Soubory
-
Co je jinak přidání souboru
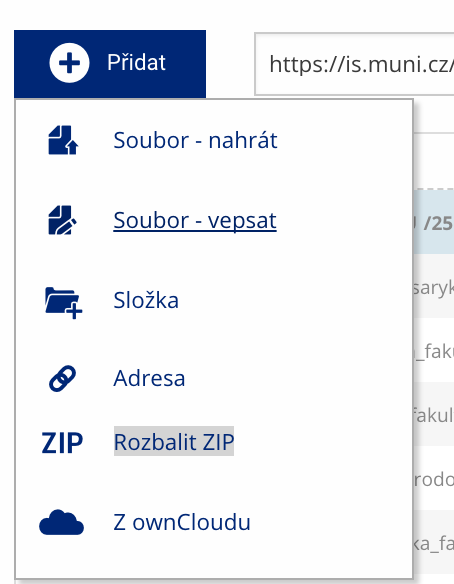 Soubor nebo složku lze nahrát pomocí tlačítka Přidat.
Soubor nebo složku lze nahrát pomocí tlačítka Přidat. -
Co je jinak další operace se soubory
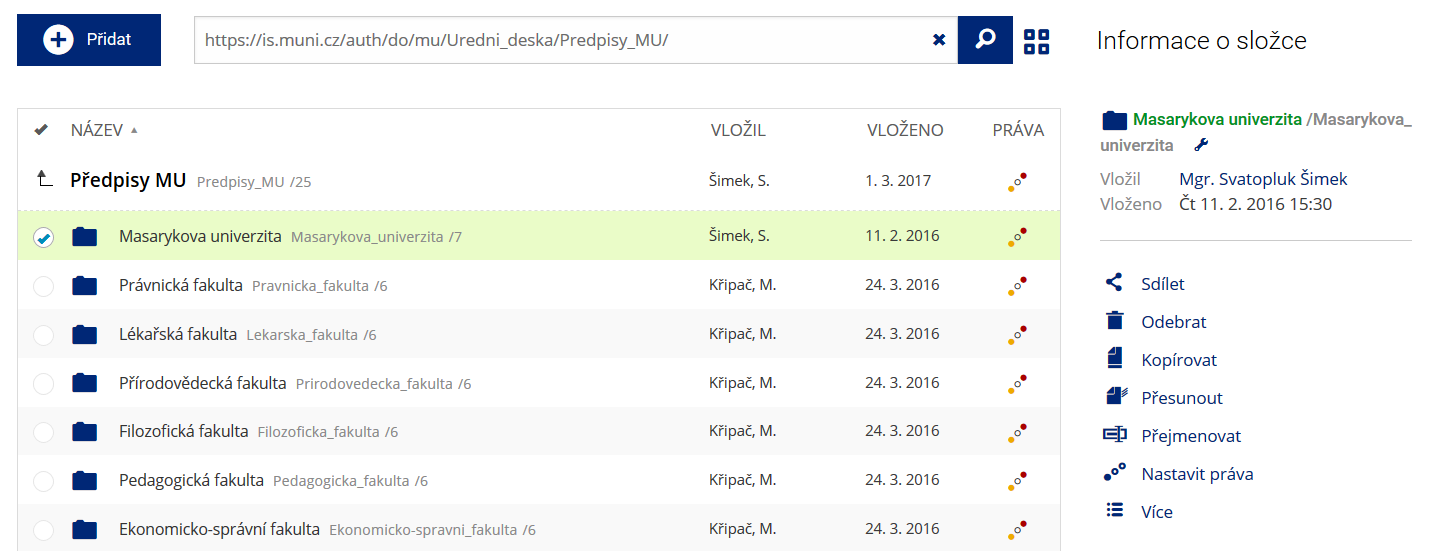 Podrobnosti lze zjistit označením příslušného řádku.
Podrobnosti lze zjistit označením příslušného řádku. -
Co je jinak pohled pro experty
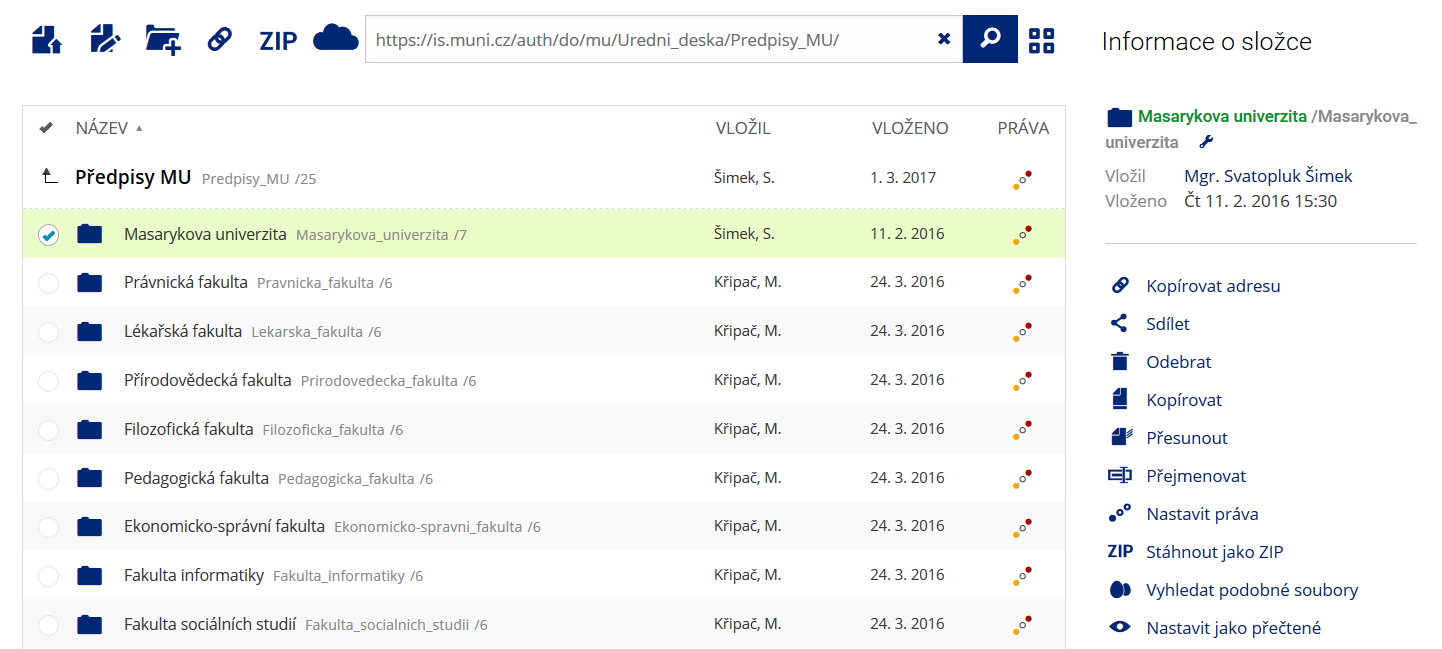 Pro častou práci je možné zvolit režim Více možností.
Pro častou práci je možné zvolit režim Více možností. -
Co je nové vyhledávání souborů
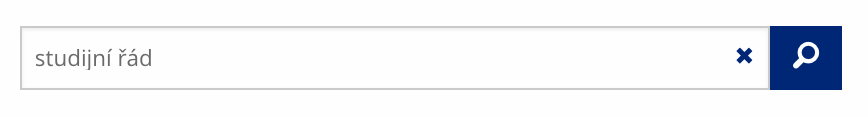 Vyhledávaný výraz můžete zadat přímo do adresního řádku.
Vyhledávaný výraz můžete zadat přímo do adresního řádku. -
Co je nové rychlý přístup k souborům
 Pomocí funkce Nedávné je možné se rychle vrátit k právě prohlíženým souborům. Oblíbené soubory je také možné označit Hvězdičkou.
Pomocí funkce Nedávné je možné se rychle vrátit k právě prohlíženým souborům. Oblíbené soubory je také možné označit Hvězdičkou. -
Co se chystá
 Připravujeme další vylepšení pro mobilní zařízení.
Připravujeme další vylepšení pro mobilní zařízení.